Student data includes clean identities, personal details, and credentials that make it useful for long-term fraud and identity theft.
EdTech Data Privacy & Security in 2026: What Schools and Vendors Must Know
- Why Data Privacy and Security Are the Top Priorities in EdTech
- The Most Common Data Risks in Educational Technology
- Regulatory Landscape: Laws, Standards & Governance for EdTech
- Best Practices for Data Protection in EdTech Tools
- How Schools Can Choose Safe and Secure EdTech Platforms
- Emerging Technologies & Their Impact on Privacy in Education
- Preparing for the Future: Strategies to Stay Ahead of EdTech Privacy Threats
- Frequently Asked Questions
The education industry in the past few years, especially post-COVID, has seen some significant changes. A definition of a classroom is no longer limited to a 4-walled space, rows of desks, a chalkboard and a teacher. With the help of technology, classrooms have transformed into something far more flexible, digital and learner-centered.
And, this is the reason why billions of students are trusting the modern ways of learning. It is expected thatby 2033, the number of mobile learning users are expected to reach 2.5 billion. (Source: Grand View Research)
But there is an issue. Learning online also puts your data at risk of unauthorized exposure. To prevent this, schools must treat student data like a high-risk asset, and vendors must bake privacy and security into product design.
In this guide, we will uncover what are the main risks associated with it, the regulatory environment, and what both schools and vendors should do right now to stay safe and trustworthy.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Schools must evaluate EdTech tools as carefully as physical learning environments.
- One wrong click can compromise an entire school network.
- Following a structured vetting checklist makes choosing EdTech tools easier.
- EdTech providers must prove privacy readiness.
- Data minimization and interoperability protect schools in the long-term.
Why Data Privacy and Security Are the Top Priorities in EdTech
Before going deep into the topic, here is a short real-life example: A student simply searched for service to get essay written, but somehow this turned into a grave mistake as he clicked on one wrong link and all his data was leaked. The aftermath? He lost control over his credentials, left a long-term digital footprint damage and his parents had to file a formal complaint to protect their son from adverse consequences. Above all, this situation left an emotional and psychological impact on him as well.
The EdTech industry deals with lots and lots of student data that includes their personally identifiable information (PII), health and special-education data, behavioral/learning analytics and even biometric or assessment data. All these factors make it a rich target for misuse and theft.
A single breach can have a severe impact on students, their families and even on the institutions they study in, triggering regulatory fines and interrupting learning at scale. This is why data privacy and security are considered the top priorities in EdTech and hence, school districts and governments increasingly require robust privacy safeguards as a procurement condition.
The Most Common Data Risks in Educational Technology
Educational technology is a vulnerable sector, surrounded by various threats at all times, making it one of the most targeted industries globally for cyberattacks. Statistics reveal that in the second quarter of 2025, the education industry faced an average of 4,388 cyberattacks per organization per week.
By understanding the common risks, you can patch up all the entryways for cybercriminals and keep your organization safe. Some common risks include unauthorized access, data breaches, insecure third-party interactions, unclear data minimization and retention, inappropriate data usage, AI/ML interference risks, and examination & integrity. Any of these can severely damage the organizational controls and reputational, disrupt learning, and platter your personal details to he wrong hands.
Regulatory Landscape: Laws, Standards & Governance for EdTech
Different countries have created a certain set of rules for the E-learning industries, that they must follow to keep the student data safe.
- United States: FERPA is the central regulatory body for education records and Copra controls the information collected from young childre. Apart from that, many US states follow their own frameworks to protect data.
- European Union: Institutions that process data of EU residents come under GDPR rules. In which, strong data subject rights, data protection impact assessments (DPIAs) and lawful bases are the key.
- West Africa & Nigeria: In past few yearas, they have updated their framework. Thre new policies make it necessary for schools and vendors to comply with the national data protection law and NDPC guidance. This significantly help students who are preparing for WAEC and NECO exams.
Apart from these, organizations such as CoSN and the Student Data Privacy Consortium publish practical guidelines and vendor checklists to ensure data protection.
Best Practices for Data Protection in EdTech Tools
So far, we have covered the common risks and reasons for breaches in the educational sector. But what precautionary steps should we take to protect our data from such risks? Well, here are some useful practices that vendors and schools alike can adopt:
- Governance & Policy: Appoint or DPO where required and maintain an up to date data inventory and flow maps.
- Technical Controls: Encryption, secure development lifecycle, role-based access control, logging and monitoring, and data anonymization are some technical controls that can proactively safeguard your credentials.
- Contractual & Operational: There are standardized, transparent data processing agreements (DPAs) that specify permitted uses, subprocessor lists, retention limits and breach notification timeline.
- Privacy by design and user controls: Configurable data retention settings for schools; parental/student consent flows and clear privacy notices in plain language.
By following these, organizations can make their security systems tenfold stronger.
How Schools Can Choose Safe and Secure EdTech Platforms
When choosing a school bus for your child, you wouldn’t just choose the shiniest one, right? There are various other factors, such as security, safety certifications, maintenance records, routes, and comfort, that need to be considered to make a wise decision.
Choosing an EdTech platform is similar. To make it easier for you, here is a complete checklist to use during procurement:
- Regulatory Fit: The vendor must meet regional legal requirements (FERPA/COPRA/GDPR/NDPA).
- Security Attestations: Ask for SOC 2/ ISO 27001 reports or third party penetration test summaries.
- Data Handling Transparency: Request an explicit DPA, subprocessor list, data party penetration test summaries.
- Minimum Data Principle: Questioning whether the product functions with minimal personal data or if it is configurable.
- Operational Readiness: Does the vendor offer admin controls, training and documentation for private privacy officers?
PRO TIP
Include a short procurement clause stating that the vendor must notify the district of any data breach within the first 72 hours and provide a remediation plan and forensic reports.
Emerging Technologies & Their Impact on Privacy in Education
We have already come so for away in the educational sector, but with advancements in technology, the future looks even more promising, especially in terms of data privacy. Emerging technologies like AL/ LLM, biometrics, neurotech and behavior analytics, and deepfakes and synthetic media will take everything further ahead, boost efficiency, personalize learning and make it much safer.
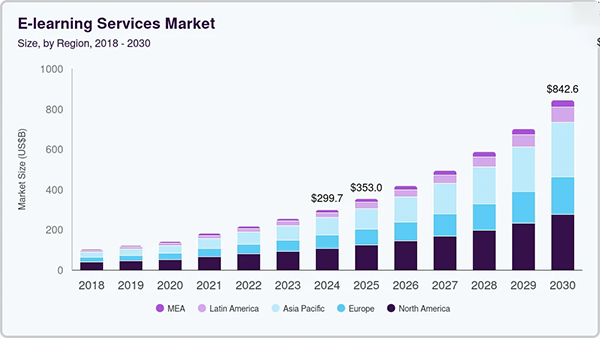
While we are on the topic, do you know that the E-learning services market was valued at USD299 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD842.6 billion by 2030.
Preparing for the Future: Strategies to Stay Ahead of EdTech Privacy Threats
For the future, both school leaders and vendors can take a few steps to stay ahead and safe against EdTech Privacy Threats:
School leaders should adopt a privacy-first procurement policy, build a vendor inventory and risk tiering, invest in staff training and digital literacy, and run tabletop exercises to test their response and communications.
On the other hand, vendors can design systems that prioritize privacy by default, operationalize compliance by keeping an up-to-date DPA, and be audit-ready by maintaining evidence from penetration tests, third-party audits, and data flow documentation.
In conclusion, it is safe to say that EdTech in 2026 will be promising and safer. By treating data protection as an educational imperative and earning trust through transparency, schools and vendors can make the whole digital learning field safer.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do attackers target student data?
What should schools ask before adopting any EdTech tools?
Before adopting any EdTech tools, schools must check for legal compliance, security attestations, data flow diagrams, AI governance policies, and a breach-notification process.
What happens if a student clicks a malicious link?
If a student falls for the trap and clicks a malicious link, it can expose hiss/her login credentials, compromise multiple systems, spread malware, and lead to broader school-wide data breaches.
What does “Privacy-by-Design” mean for EdTech?
In EdTech, privacy by design means that platforms are built from the ground up with safeguards like limited data collection, encrypted storage, consent controls, and clear retention rules.
Most people think hackers need advanced tools to find security gaps. Sorry to break the news, but sometimes, Google is…
If you are a part of any business, you might have attended meetings. And in case you were connected to…
SSD data recovery software can retrieve data that has been deleted, damaged, or otherwise rendered inaccessible from the SSD hard…
How can I improve the performance and grow my business? My team is already occupied with several projects, how do…
It feels very frustrating to lose all your digital data due to just one panic mistake of selecting a password…
Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) are a type of legally structured company. They are created by parent companies, usually with temporary…
Web cache and cookies make browsing faster by saving logins, settings, and site data. But over time, they can slow…
Finding the best tools for your company feels like a big job. You need systems that actually help your team…
In the digital age, instant messaging apps have become an essential part of our daily communication. Whether for personal use,…