Almost everything we do now happens online, be it banking, shopping, or corporate work systems, making cybersecurity a crucial element today.
Why Cybersecurity Is the Backbone of Modern Technology
- 1. The Digital Expansion and Its Hidden Vulnerabilities
- 2. The Growing Complexity of Cyber Threats
- 3. Cybersecurity as the Foundation of Trust in Technology
- 4. Protecting Data: The Core of Every Security Strategy
- 5. The Role of Cybersecurity in Emerging Technologies
- 6. The Economic Impact of Cybersecurity
- 7. Building a Culture of Cyber Awareness
- 8. Collaboration and Adaptability are the Future of Cybersecurity
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
You use your phone every day. That’s technology!
You scroll social media. Send messages, make payments digitally, order food online, log in to work portals, attend virtual meetings, store files on the cloud, you’re reading this blog, and whatnot. All this? Just because of technology again.
Think about it, from the moment you wake up to when you fall asleep, you are using technology in some way or the other. And this is where cyber attackers with malicious intent come into the picture. They are like pests waiting for one slip-up to infect your systems. Nearly 9 out of 10 organizations reported experiencing a cybersecurity incident in the past year. (Source: Bluefire Redteam)
And this is why cybersecurity has become the ultimate key that keeps modern systems running safely. Without it, the entire digital ecosystem would collapse in a minute.
In this post, we will dive deeper into the subject and understand why cybersecurity is the true backbone of technology and how it shapes trust, innovation, and the digital global economy.
Key Takeaways
- Technology runs our lives today, and cybersecurity keeps it running safely.
- Cyber threats are growing smarter, faster, and harder to avoid.
- Trust in digital platforms exists because strong security exists behind them.
- Investing in cybersecurity costs less than recovering from a breach.
- The future of technology depends on secure, ethical innovation.
1. The Digital Expansion and Its Hidden Vulnerabilities
We have moved past the times when all the industries, be it finance, healthcare, education, retail, and logistics, relied on manual records and effort to function; they have migrated to digital platforms.
No doubt, this expansion delivers unmatched efficiency. But at the same time, it brought new vulnerabilities with it.
Cloud storage, IoT devices, and remote collaboration tools handle massive amounts of data that are often targeted by cybercriminals. Legacy systems often struggle to keep up with modern threats. Users unknowingly expose themselves through weak passwords, unsafe networks, and phishing traps.
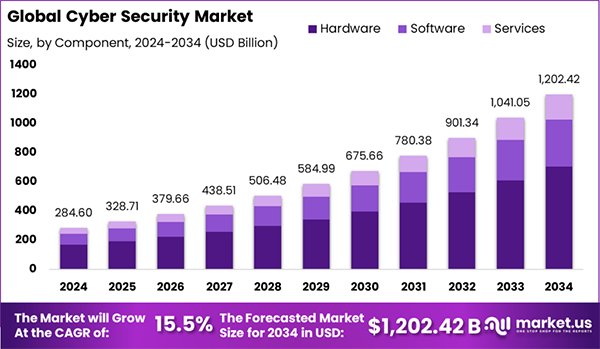
In short, the more connected we become, the more doors open to new vulnerabilities. And due to these vulnerabilities, the global cybersecurity market is on the rise and is expected to hit USD 1,202.42 billion by 2034.
2. The Growing Complexity of Cyber Threats
As we move forward and bring in stronger defenses for our digital systems, the cyber threats follow closely. Once, cyberattacks were simple viruses, but today they have turned into sophisticated and multi-layered operations.
Ransomware-as-a-service, advanced persistent threats (APTs), supply chain attacks, identity thefts, and AI-powered exploits are some common modern threats. To fight these, organizations now rely on cybersecurity exposure management as they help continuously identify, measure and mitigate these vulnerabilities before they escalate and turn into something more damaging.
If you wish to learn more about it in depth or wish to pursue a career in this field, you can enroll in an online masters of cybersecurity.
3. Cybersecurity as the Foundation of Trust in Technology
Here is a choice for you:
Option A: A mobile app to make payments, but it has no two factor authentication, no privacy police and has faced several data leaks in the past.
Option B: Using a payment platform that encrypts your data, requires identity verification, alerts you about suspicious activity and openly explains the policies protecting your sensitive information.
Which one would you choose? Most people would go for option B because it is clearly more trustworthy and reliable. Trust in technology is not just about amazing features. It comes with knowing that your data is protected and your identity is secure at all times.
Without strong defenses protecting their data, users lose confidence, which corresponds to businesses losing customers and the whole system breaks down. Hence, trust and cybersecurity are inseparable.
4. Protecting Data: The Core of Every Security Strategy
Cybercriminals are well aware of the fact that data is the world’s most valuable digital asset. This is why, to keep it safe, a strong cybersecurity strategy should focus on data encryption, access control, identity management, backup and disaster recovery, real-time threat monitoring and endpoint protection.
DO YOU KNOW?
An average person has over 100 online accounts across different platforms, yet most reuse the same password for all their accounts, making one small leak a big problem for them.
5. The Role of Cybersecurity in Emerging Technologies
Modern innovations like AI, 5G, robotics, blockchain, and smart devices rely heavily on cybersecurity, and each of these are associated with different risks. For example, AI can be manipulated through adversarial attacks, IoT devices can be exploited through weak firmware, autonomous vehicles depend on secure communication and 5G expands the attack surface significantly.
This is why, cybersecurity is important, it ensures innovation move forward safely and without introducing unacceptable risks.
6. The Economic Impact of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is not just a technology requirement, but an economic necessity as well. Every year, billions of dollars are lost due to downtime, data loss, regulatory penalties and damage to brand reputation as a result of cyberattacks
Investing in strong cybersecurity measures is always better and more cost effective than recovering from a major breach. Investing in cybersecurity systems helps companies enjoy reduced operational risks, lower long-term costs, higher customer trust and stronger competitive advantage
7. Building a Culture of Cyber Awareness
Technology cannot do all the work itself; there must be human force trained to be cyber-aware. In every organization, there should be:
- Regular employee training
- Secure password practices
- Phishing awareness programs
- Incident reporting protocols
- Responsible use of digital tools.
With these, every employee will understand their role and security will become a shared responsibility rather than just a burden for IT departments.
8. Collaboration and Adaptability are the Future of Cybersecurity
The future of cybersecurity is all about global collaboration, continuous learning and ethical innovation. For this:
- Governments, corporations, and cybersecurity teams must share threat intelligence.
- Organizations will rely more on predictive analytics and AI-powered defense systems.
- Innovation must remain ethical, ensuring privacy and transparency.
- Tools like quantum computing simulator will help prepare security systems for the next era, when quantum technology could break today’s encryption.
It is safe to say that adaptability and cooperation will define the next generation of cybersecurity defense.
Conclusion
Technology is like a constant background song in our lives that makes our lives much sweeter and easier but at the same time brings various risks as well. That is why cybersecurity is no longer optional; it is the backbone of modern technology and the foundation of trust in this digitally driven world.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is cybersecurity so important today?
Is cybersecurity only a concern for big companies?
Absolutely not. Cybersecurity should be a priority for individuals, small businesses, startups and large enterprises; basically for everyone.
What happens when cybersecurity is weak?
Weak cybersecurity systems open the door to various operational issues like data breaches, financial loss, identity theft, system downtime, and loss of customer trust.
How does cybersecurity affect everyday users?
Cybersecurity is equally important for everyday users. It protects their personal passwords, personal details, payment information, emails, and online accounts.
Why can I not connect to Wi-Fi on my iPhone? It is frustrating, but the good news is that most…
With the rise of distributed systems, microservices, and cloud-native architectures, the sheer amount of telemetry data being generated is staggering.…
Managing files and folders is a core part of working with Linux. One skill every user should know is how…
Your digital life also runs on small settings most people ignore. Think of your online life like an apartment. You…
The use of SD card recovery software allows you to restore pictures, videos, and document files that have been deleted…
Stressed by too many emails in Outlook? Fix that properly by learning how to mass delete emails on Outlook. A…
Managing payroll is one of the most complex administrative responsibilities for businesses. Beyond calculating wages and issuing paychecks, payroll teams…
Linux data recovery software programs allow users to recover deleted, corrupted, and lost files from their Linux storage device(s) (HDD,…
Managing teams and operations in an aligned way is much more complex than it seems. However, the use of specialized…









