It is a part of the data analysis process, which involves organizing data and establishing relationships in a database.
What is Data Normalization? Organize and Optimize Your Database
- What is Data Normalization in Databases?
- What are the 4 Types of Data Normalization?
- What are the Rules for Normalization of Database Tables?
- Database Normalization: Popular Methods or Techniques
- 3. Decimal Scaling Normalization
- What are the Benefits of Database Normalization?
- What are some Challenges of Data Normalization?
- Final Thoughts
- Frequently Asked Questions
As someone who has worked closely with data sets and analytics, I have seen how disorganized data can limit even the best tools. With the big data transforming strategies (its market is projected to cross $90 billion in 2025), maintaining accuracy and consistency has become essential.
That is where data normalization comes in. It is a process used to make sure that the data collected is structured, reliable, and ready for analysis.
I am here to share my experience and provide you with everything important to learn about the normalization of databases, including their methods, rules, processes, examples, and more.
What is Data Normalization in Databases?

Database normalization is like arranging your database or information in a neat, consistent, and easy-to-find way. It reduces duplicate data, avoids errors, and makes your database faster and easier to manage.
In the process, data is stored in tables, with connections between them to avoid repeating the same information. Every entry is structured in the same way. Standardization of all variables (like recording names, addresses, contact information, or product codes).
Let’s try to simplify “What is database normalization and why does it matter?”. If your business wants accurate reporting, smoother analytics, and reliable insights, normalization is a must. Otherwise, it increases the chances of errors when data is added, changed, or removed.
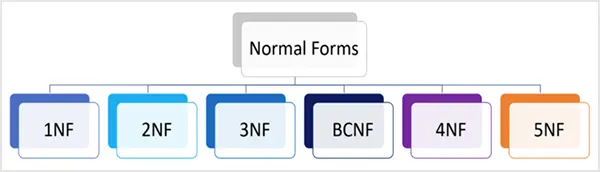
What are the 4 Types of Data Normalization?
Normalization of a database is not random. It follows rules called normal forms, and each ‘normal form’ builds on the previous one. Here are the four most common database normalization types:
- First Normal Form (1NF)
This type of normalization makes sure each field has a single value, and each record is unique.
- Second Normal Form (2NF)
This form builds on the rules of the 1NF. Plus, it ensures that every piece of data depends entirely on the primary key. The primary key is the main unique identifier of the data table.
- Third Normal Form (3NF)
Again, this adheres to all the above rules and removes any dependencies between non-key attributes, keeping data independent and organized.
- Boyce and Codd Normal Form (BCNF/3.5NF)
Boyce-Codd Normal Form is also known as 3.5NF because it is a developed version of the third form (required in only special cases). Its unique rule is that it strengthens 3NF by making sure every determinant is a candidate key. A candidate key can be any column or set of columns that can uniquely identify rows.
These steps help analysts create a clean, efficient, and reliable database table and normalization.
What are the Rules for Normalization of Database Tables?
I know you must be confused between the types, forms, and rules of normalization. Let’s break down the main rules in simple terms with data normalization examples.
Here’s how to normalize data in simple steps:
1. First Normal Form
Here, the objective is to make sure that there are no repeated values, and every field has one value.
Example:
| Order ID | Consumer Name | Products Purchased |
| 101 | William Sebastian | Bottle, Tumbler |
| 102 | Nancy Smith | Tiffin Box, Mug |
Problem: Multiple products in one field.
Solution to normalize data: Split them into atomic values.
| Order ID | Consumer Name | Products Purchased |
| 101 | William Sebastian | Bottle |
| 101 | William Sebastian | Tumbler |
| 102 | Nancy Smith | Tiffin Box |
| 102 | Nancy Smith | Mug |
2. Second Normal Form
The goal in this form of database table normalization is to ensure that all non-key fields fully depend on the primary key.
| Student ID | Course ID | Student Name | Course Name |
| 501 | MPC01 | George | History |
| 502 | MPC02 | Robert | Geography |
Problem: Student Name depends only on Student ID, and Course Name depends only on Course ID. They are not fully dependent on the combination.
Solution to normalize data: We need to split the data into three separate tables.
- Student Data
Student ID Student Name 501 George 502 Robert
- Course Data
Course ID Course Name MPC01 History MPC02 Geography
- Enrollment Data/Bridging Table
Student ID Course ID 501 MPC01 502 MPC02
3. Third Normal Form
This form now allows any transitive dependencies, which means that non-key fields should not depend on other non-key fields.
| Employee ID | Name | Department | Salary | Tax Rate |
| 1001 | Graham | Finance | 8000 | 15% |
| 1002 | Donald | Sales | 7500 | 10% |
Problem: Tax Rate depends on the Salary filed, but Employee ID does not.
Solution to normalize data: Again, in this database normalization example, you need to make three separate tables.
- Employee Data
Employee ID Name Department 1001 Graham Finance 1002 Donald Sales
- Salary Data
Employee ID Salary 1001 8000 1002 7500
- Tax Data
Salary Tax Rate 8000 15% 7500 10%
4. Other Forms of Database Table Normalization (If required)
Usually, you won’t have to go for these forms. However, some data might need further normalization. We have three popular forms for those data sets:
- Boyce-Codd Normal Form (BCNF) for strengthening 3NF by ensuring every determinant is a candidate key.
- Fourth Normal Form (4NF) handles multi-value dependencies for complex many-to-many relationships.
- Fifth Normal Form (5NF) helps in removing join dependencies while keeping data integrity intact.
So, these are the steps you need to take for effective SQL data normalization. Even if your database is small now, the normalization of data prevents headaches later.
Database Normalization: Popular Methods or Techniques
The above method for the normalization of databases is not the only technique in this playground. There are two main sides of normalization: Structural and Statistical (used in analytics and machine learning).
Here’s a quick look at some of the most popular methods used in scaling statistical data:
1. Min-Max Normalization
Min-max normalization scales your data to a fixed range, often between 0 to 1. Each value is adjusted using the smallest and largest values in the dataset. This is helpful when data needs to be compared on the same scale.
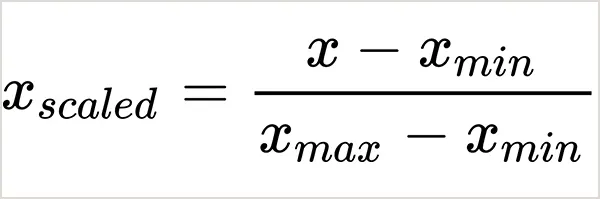
2. Z-Score Normalization
Z-score normalization is also known as standardization. This method adjusts values based on how far they are from the average (mean) in terms of standard deviation. The Z-score method is useful when data follows a normal (bell-shaped) distribution.
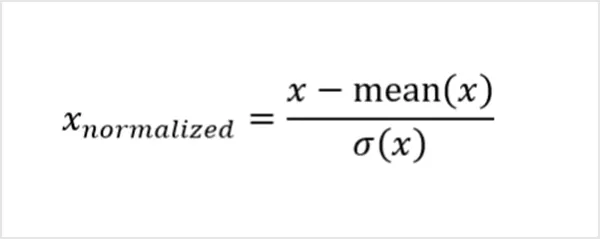
3. Decimal Scaling Normalization
Decimal scaling shifts the decimal point of data values by dividing them by a power of 10, usually based on the largest value in the dataset. It brings all numbers into a smaller range, often between -1 and 1.
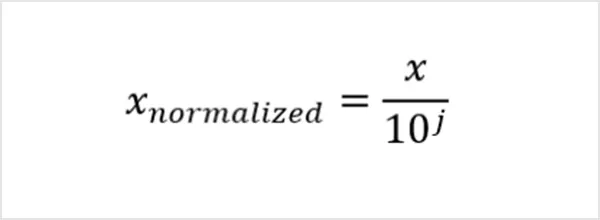
Each technique serves a specific purpose, while database normalization ensures data consistency, scaling methods make numerical data ready for analysis, and machine learning.
What are the Benefits of Database Normalization?
When done right, data normalization can transform messy and duplicate data into a clean and high-performance system. Here’s why it is important for any data setup:
- More storage space: Eliminating duplicate and unnecessary data saves massive storage, especially in large databases. Less clutter also means faster loading times and better processing.
- Faster queries and analysis: With organized data, systems can fetch results in seconds. Teams spend less time fixing broken data and more time drawing insights that actually matter.
- Improved consistency and integrity: It also ensures that every record is reliable, resulting in fewer errors and cleaner reports.
- Smarter segmentation: Do you want to target leads by different variables? Normalized data makes this effortless. You can split and group data accurately, which is really a huge win for marketing and operations.
- Easier Maintenance: With smaller and well-structured tables, updates and edits become simple. You can add, change, or delete data without any hassle.
What are some Challenges of Data Normalization?
Now that you have learned “What is normalization of databases?”, you should also know that it is not magic. It has its own hurdles; here are a few things to watch out for in the process:
- Splitting data into multiple tables can lead to insert or update anomalies if relationships are not defined properly. It is crucial to set clear primary and foreign keys.
- Sometimes, highly normalized databases can slow down complex queries due to multiple joins of tables.
- Designing a normalized database involves a deep understanding of your data relationships. It is not hard once you know the rules, but it does require planning and time.
- Denormalization might be necessary for some data. However, it can also lead to data integrity issues and anomalies. Thus, it is important to be more careful while doing denormalization.
You should keep these things in mind before handling and normalizing any data to maintain a balance between integrity and performance.
Final Thoughts
In my books, data normalization is the backbone of reliable data management. When your data is normalized, it is consistent, organized, and easy to use across systems.
However, keep in mind that as you add more data sources, maintaining normalization gets trickier. Still, the effort pays off in multiple ways. So, if you want your data to really work for you, it is not optional, but essential.
Frequently Asked Questions
What do you mean by data normalization
How to normalize data in Excel?
You can use the Min-max and Z-score normalization method to normalize data in Microsoft Excel.
What data anomalies does database normalization prevent?
Normalization prevents three main types of anomalies: insertion, deletion, and update anomalies.
What are the methods for normalizing data?
1NF, 2NF, and 3NF are the most used methods for normalizing databases. Min-max, z-score, and decimal scaling are the popular techniques used in statistical normalization.
Why is data normalization useful?
It is useful because it helps in improving data accuracy, making data integration and analysis easy, and reducing data anomalies.
Why can I not connect to Wi-Fi on my iPhone? It is frustrating, but the good news is that most…
With the rise of distributed systems, microservices, and cloud-native architectures, the sheer amount of telemetry data being generated is staggering.…
Managing files and folders is a core part of working with Linux. One skill every user should know is how…
Your digital life also runs on small settings most people ignore. Think of your online life like an apartment. You…
The use of SD card recovery software allows you to restore pictures, videos, and document files that have been deleted…
Stressed by too many emails in Outlook? Fix that properly by learning how to mass delete emails on Outlook. A…
Managing payroll is one of the most complex administrative responsibilities for businesses. Beyond calculating wages and issuing paychecks, payroll teams…
Linux data recovery software programs allow users to recover deleted, corrupted, and lost files from their Linux storage device(s) (HDD,…
Managing teams and operations in an aligned way is much more complex than it seems. However, the use of specialized…









