Data privacy is the process of gathering, storing, sharing, and safeguarding private and sensitive information so that it is used appropriately and exclusively for the intended purpose.
What is the Future of Data Privacy? 4 Things You Need to Know About Data Privacy
What comes to your mind when you hear the term ‘data privacy’? Most would think of personal details, names, passwords, financial information, and the fear of those details falling into the wrong hands. And, it is absolutely correct, but it is not all; it extends far beyond that.
Today, data is the most valuable currency, and it influences how businesses operate, how governments regulate technology, and how much control individuals truly have over their digital lives.
But here’s the concerning part: still, the majority of the companies lack robust frameworks, and 68% globally worry about their online privacy. (Source:Data Privacy Statistics)
Fortunately, as we are moving ahead, data privacy is steadily shifting from a reactive concern to a built-in concern. Which means that the future of data privacy will be stronger and proactive. Want to take a glimpse into that future? Keep reading!
Key Takeaways
- Data privacy is becoming a key business strategy rather than just a compliance task.
- The future of security is being shaped by identity-first and zero-trust security models.
- By restricting needless data access, micro segmentation lowers risk.
- Verification and recovery of backups are essential to privacy resilience.
- AI will increase data security while posing new privacy issues.
What is the Future of Data Privacy?
The future of data privacy is all about proactive protection, real-time monitoring, and privacy-by-design strategies. Unlike the traditional methods, we will no longer sit back and wait for data breaches to take action. Instead, security systems in an organization will be trained to anticipate risks and embed privacy into each and every layer of their digital infrastructure.
Micro-Segmentation and Continuous Authentication Trends
Protecting data works best when trust is granted in small, verified steps, the same way networks are divided into smaller, isolated segments instead of relying on one single security perimeter. Micro-segmentation limits how far attackers can move if they gain access to one area, reducing the damage even if the password is compromised.
In combination with this, continuous authentication is gaining momentum. So, no, even if someone successfully logs into your system, they will need to continuously go through identity verification.
Think of it like burglars trying to break into a building, but they find a locked door every five minutes. The probability of them getting caught before inflicting any real damage increases significantly.
Backup Verification and Restore Testing as Part of Privacy Resilience
What would the systems protect if there is no data? This is why, even if the data is well encrypted and protected, it loses its value if it cannot be restored after a ransomware attack or system failure. As a result, backup verification and restore testing prove to be two of the essential components of privacy resilience.
This is why organizations have started relying on verified backups to ensure that personal and sensitive data remain accessible even after a breach.
Cloud Misconfiguration Risks and the Need for Automated Remediation
Cloud adoption continues to grow, and why wouldn’t it? The convenience it brings is unmatchable. But at the same time, misconfigurations remain one of the leading causes of data exposure.
To fight this, automated remediation tools that can detect and fix misconfigurations in real time are introduced in the systems.
PRO TIP
Instead of viewing data inventories as static documents, start treating them as dynamic systems. It is much simpler to adjust to future privacy regulations, AI usage guidelines, and automated security controls when the locations of data creation, transfer, and storage are regularly mapped.
4 Things You Need to Know About Data Privacy
Here are the key factors influencing privacy practices globally as data ecosystems change. Understanding these will help organizations create tighter and harder-to-bypass security systems.
1. Regulations Will Become More Complex and More Strict
Data is an extremely important asset today. And that is why regulations pertaining to data privacy are growing in both industries and geographical areas. And organizations dealing with customer confidential information must follow certain regulations for consent transparency, breach reporting, and data retention are being introduced by laws like the CCPA, GDPR, and new international frameworks.
Compliance won’t be a one-time task in the future. To avoid fines and reputational harm, organizations must constantly monitor regulatory updates and modify policies, procedures, and technologies as necessary.
2. Zero-Trust and Identity-First Security Will Define the Future
Even within internal networks, zero-trust security models make the assumption that no user or device should be trusted by default. Verification, authentication, and authorization are required for each access request.
This strategy is strengthened by identity-first security by making identity the central control point for data access. If combined with secure network practices, such as anonymized traffic and controlled access tools from providers like BestProxy, organizations can significantly reduce exposure and maintain operational flexibility at the same time.
3. Backups, Encryption, and Data Recovery Will Be Mission-Critical
Encryption by itself is not enough anymore. Future-proof privacy plans use encryption, secure backups, and recovery plans that have been tested. If encrypted data is lost or corrupted, organizations must be able to restore it quickly without compromising integrity or compliance.
Data recovery capabilities will increasingly be viewed as part of privacy obligations, especially in industries handling financial, healthcare, or personal identity data
4. AI Will Shape Both Data Protection and New Privacy Risks
Artificial intelligence is transforming data privacy in two ways. On one hand, AI-powered tools improve threat detection, automate compliance monitoring, and identify unusual access patterns. On the other hand, it introduces new risks, such as unauthorized data scraping, deepfake misuse, and excessive data collection.
Balancing AI innovation with ethical data usage and privacy safeguards will be a major challenge.
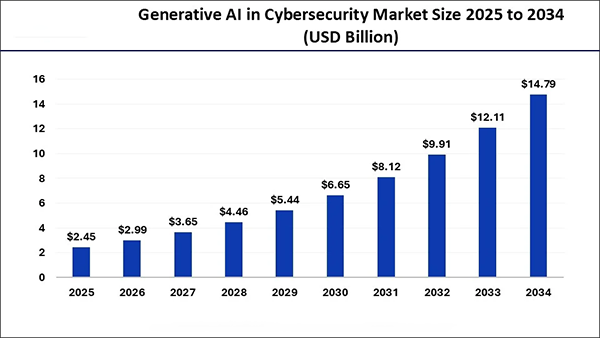
Generative AI will play a crucial role in data privacy in the future, and hence the Gen AI in the cybersecurity market is on the rise and is expected to reach $14.79 billion by 2034, from $2.25 billion in 2025.
Conclusion
Data privacy will be proactive, flexible, and closely linked to corporate strategy in the future. Organizations need to reconsider how they safeguard sensitive data, from micro-segmentation and zero-trust models to automated cloud remediation and AI-driven security with the help of platforms like Aproxy.
Businesses can develop privacy resilience and uphold trust in an increasingly data-driven world by keeping up with regulatory trends, fortifying identity-based access controls, verifying backup systems, and utilizing reliable infrastructure solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is data privacy?
Why is data privacy more crucial now?
Data privacy is crucial for preventing breaches, satisfying legal requirements, and upholding user trust as data volumes increase and upholding user trust as data volume increase and cyber threats change.
In what ways do continuous authentication and micro-segmentation enhance privacy?
By segmenting systems into smaller parts and constantly conforming to user identity, they restrict access to data and lessen the impact of unauthorized access.
How will AI impact data privacy going forward?
While AI will improve threat detection and compliance automation, it also creates new privacy risks that call for more robust governance and moral protections.
Why can I not connect to Wi-Fi on my iPhone? It is frustrating, but the good news is that most…
With the rise of distributed systems, microservices, and cloud-native architectures, the sheer amount of telemetry data being generated is staggering.…
Managing files and folders is a core part of working with Linux. One skill every user should know is how…
Your digital life also runs on small settings most people ignore. Think of your online life like an apartment. You…
The use of SD card recovery software allows you to restore pictures, videos, and document files that have been deleted…
Stressed by too many emails in Outlook? Fix that properly by learning how to mass delete emails on Outlook. A…
Managing payroll is one of the most complex administrative responsibilities for businesses. Beyond calculating wages and issuing paychecks, payroll teams…
Linux data recovery software programs allow users to recover deleted, corrupted, and lost files from their Linux storage device(s) (HDD,…
Managing teams and operations in an aligned way is much more complex than it seems. However, the use of specialized…









